Welcome to the Ultimate Guide to Site Map Creation & SEO Tips. This guide will show you how site maps boost your website’s visibility. It helps search engines crawl and index your site better. Whether you’re new to site map creation or want to improve, you’ll find useful tips here.
A site map is key for search engines to navigate your website. It organizes your pages, making it easy for search engines to find and index your content. This boosts your site’s visibility in search results and ensures important pages are seen first.
To make a site map, you need to outline your website’s sections and pages. There are different types, like XML sitemaps and HTML sitemaps. XML sitemaps are for search engines, while HTML sitemaps help users navigate your site.
For better visibility, create an SEO-friendly site map. Organize your content well, use the right keywords, and make sure your site map supports your website’s goals.
In this guide, we’ll cover all about site map creation and SEO tips. You’ll learn about:
- What a site map is and why it’s important
- Who needs a site map and when to make one
- What to include in a site map for better crawling and indexing
- The parts of a site map and how to make one
- How to submit your site map to search engines
Key Takeaways:
- A site map is vital for better website visibility and search engine crawling and indexing.
- Creating an SEO-friendly site map means organizing content well, using keywords, and aligning with your site’s goals.
- Site maps help search engines understand your website’s structure and prioritize valuable pages.
- Only include indexable pages with valuable content in your site map.
- Submitting your site map to search engines improves your website’s visibility and indexing.
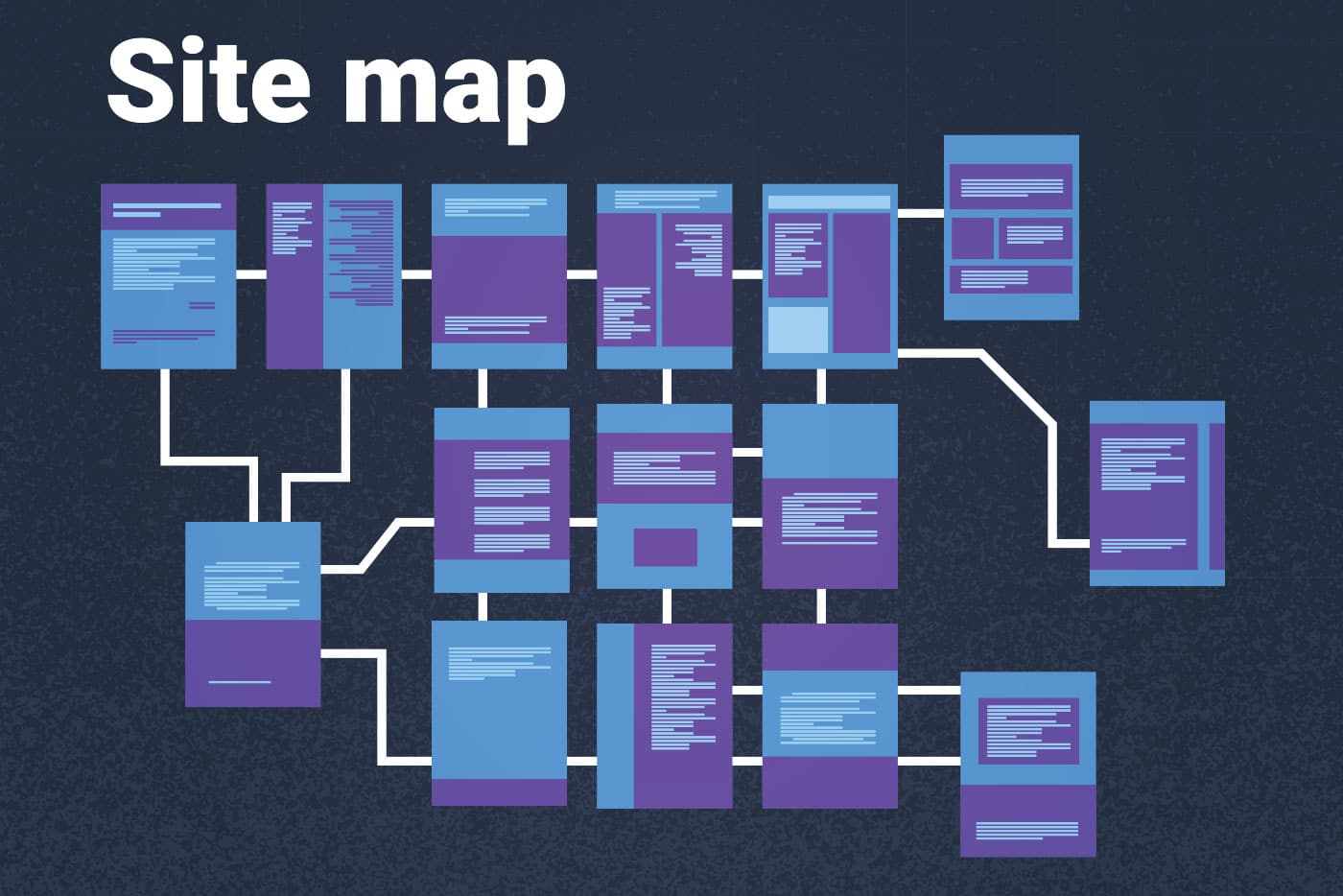
What is a Sitemap?
A sitemap is a key tool for website optimization. It’s an XML or HTML file that guides search engine bots through your website. By listing all your URLs, a sitemap helps search engines find and index your most important pages.
Search engine bots use sitemaps to navigate your website. Without one, they might miss pages or sections, leading to poor indexing and lower visibility in search results.
There are two main types of sitemaps: XML sitemaps and HTML sitemaps. XML sitemaps are for search engine bots, while HTML sitemaps help users. Both improve website indexing and SEO.
Sitemaps have their own URLs and should be in your website’s root directory for better visibility. You can also link to your sitemap in the robots.txt file to help search engine bots find it.
A sitemap acts as a roadmap for search engine bots, ensuring they reach and index the most valuable pages on your website.
The Importance of Sitemaps for Website Indexing
Sitemaps are key for website indexing. They help search engine bots find and index your site’s pages. By listing all URLs, sitemaps show bots which pages are most important.
Without a sitemap, bots might miss some pages. This is true for sites with complex structures or isolated pages. Adding these pages to your sitemap boosts their chances of being indexed and seen in search results.
Sitemaps also manage crawl budget better. This is the number of pages bots can check in a set time. By showing which pages are most important, you guide bots to focus on the best ones.
Also, sitemaps give you feedback from search engines. This helps you spot and fix any crawling or indexing problems.
Next, we’ll explore why sitemaps are good for your website’s SEO.

Why are Sitemaps Useful?
Sitemaps are key to helping search engines find and index your website better. They offer many benefits that boost your site’s visibility and performance. Here’s why sitemaps are so valuable:
- Optimizing Search Engine Crawling: Search engine crawling is how search engines find and check your website’s content. A sitemap gives search engines a clear guide to crawl your site well. This makes sure search engine bots can find and access all your site’s important pages, even if it’s complex.
- Ensuring Indexing of Valuable Pages: Sitemaps help search engines focus on your most important pages. When they crawl your sitemap, they know which pages to prioritize. This is key if your site has lots of pages or specific pages you want to highlight.
- Optimizing Crawl Budget: Search engines have a limited crawl budget for each website. A detailed sitemap helps search engine bots focus on your site’s most important pages. This makes the most of the crawl budget and avoids wasting time on less important pages.
- Facilitating the Indexing Process: Sitemaps speed up the indexing process by giving search engines key metadata about your site. This includes when each page was last updated and its priority. This helps search engines understand your pages’ importance and relevance, leading to faster and more accurate indexing.
- Receiving Search Engine Feedback: When search engines crawl your sitemap, they give you feedback on the URLs they found. This feedback helps you spot any crawling problems or errors. Fixing these issues ensures search engines can effectively crawl and index your website’s content.

Using sitemaps is key for a good SEO strategy. A well-made sitemap helps search engines find and list your site better. This makes your site more visible and brings more visitors to your important pages.
Who Needs a Sitemap?
Every website can use a sitemap, but some really need it. You should make a sitemap if your site is one of these:
- Websites with dynamic content: If your site often changes, a sitemap helps search engines keep up with the updates.
- Large websites with many pages: Big sites need sitemaps to help search engines find and list all their valuable content.
- New websites with few external links: New websites are harder for search engines to find. A sitemap makes it easier for them to index your site.
- Websites with isolated or poorly linked pages: If your site has hard-to-find pages, a sitemap helps search engines discover them.
- Websites with rich media content: Sites with lots of images and videos can use sitemaps to help search engines understand and index this content.
Creating a sitemap helps search engines crawl and index your site better. This makes your site more visible and easier for users to find.

What to Include in a Sitemap?
To make a good sitemap, you need to pick the right stuff and leave out the wrong stuff. This helps search engines find and index your site’s best pages. Here’s what you should think about:
- Indexable Pages: Only include pages that search engines can index. These pages should have URLs that search engines can crawl. Make sure they’re not blocked by robots.txt or meta tags.
- Valuable Content: Put in pages with great and relevant content. These pages should help your site’s goals and match your target keywords.
- Avoid Thin or Duplicate Content: Thin or duplicate content should be left out. These pages might not be worth much to search engines or users. They can cause problems with indexing.
- Avoid Paginated Pages: Paginated pages, like those with lots of product or article pages, shouldn’t be in your sitemap. Focus on the main content pages instead.
- Avoid Parameter or Session ID-based URLs: Exclude pages with URLs that have parameters or session IDs. These can cause duplicate content problems or extra crawling.
- Avoid Site Search Result Pages: Don’t include pages that show search results on your site. These pages might not have much content and can confuse search engines.
- Avoid Archived Pages: If you have archived pages that are old and not useful, don’t include them in your sitemap. They can hurt your indexing efforts.
By picking the right indexable pages with valuable content and leaving out thin or duplicate content, paginated pages, parameter or session ID-based URLs, site search result pages, and archived pages, you can improve your site’s visibility. This makes it easier for search engines to index your site.
| Content to Include | Content to Exclude |
|---|---|
| Indexable Pages | Thin or Duplicate Content |
| Valuable Content | Paginated Pages |
| Parameter or Session ID-based URLs | |
| Site Search Result Pages | |
| Archived Pages |
Curating your sitemap to include the right content and exclude unnecessary or low-quality pages can help improve the indexing and visibility of your website.

Sitemap Components
Sitemaps have different XML tags for various parts. These tags help organize and structure the sitemap. They make it easier for search engines to understand and navigate your website.
The main tags used in XML sitemaps are:
- <?xml>: Specifies the XML version and encoding for the sitemap.
- <urlset>: The root tag that encapsulates all the URLs in the sitemap.
- <url>: Represents an individual URL on your website.
- <loc>: Specifies the URL itself, indicating the web page’s address.
- <lastmod>: Indicates the last modification date of the web page.
- <changefreq>: Describes the change frequency of the web page, helping search engines understand how often the content is updated.
- <priority>: Assigns a priority level to the web page, indicating its relative importance compared to other pages on your site.
- <hreflang>: Used for international SEO to specify language versions of the web page.
The <urlset> tag holds all the URLs in a sitemap. The <url> tag is for each URL. Inside the <url> tag, the <loc> tag shows the URL itself. The <lastmod> tag shows when it was last updated.
The <changefreq> tag tells how often the page changes. The <priority> tag sets a priority level for the page. The <hreflang> tag is for language versions for international SEO.
Knowing these XML tags helps you make a good sitemap. This improves search engine crawling and indexing for your site.
Sitemap Extensions
Sitemaps can include extra info for rich media content. These extras help search engines find and show your multimedia better. Here are some examples:
XML Image Sitemap
The XML Image Sitemap gives info about your website’s images. It includes image URLs, captions, and titles. This helps search engines index your images better.
It makes your images more visible. It also helps them show up in image search results.
XML Video Sitemap
The XML Video Sitemap gives details about your website’s videos. It includes video URLs, titles, and descriptions. This ensures search engines index and display your videos right.
This is great for sites with lots of videos. It helps people find your videos easier.
Google News Sitemap
The Google News Sitemap is for news sites. It helps your news articles show up in Google News. It includes info like publication dates and keywords.
This boosts your news content’s visibility. It makes it more likely to appear in news searches.
Using these extensions can improve your rich media content visibility. This includes images, videos, and news articles. It makes sure search engines can rank and display your content well.
How to Create a Sitemap?
Creating a sitemap can be done in several ways. You can choose manual creation or automated methods. Let’s look at the options:
1. Creating a Sitemap Manually
If you know how, you can make a sitemap by hand. This lets you control the sitemap’s structure and content. It ensures your sitemap matches your website’s organization.
2. Creating a Sitemap Automatically
Some CMS or eCommerce platforms can make a sitemap for you. They have features that automate sitemap creation. Check your platform’s settings to see if this is available.
There are also plugins for popular CMS platforms. These plugins make creating a sitemap easy. They offer simple interfaces and automated creation.
3. Using Third-Party Tools
If you’re not using a CMS or eCommerce platform or prefer a more customizable approach, third-party tools for creating sitemaps are great. These tools offer advanced features and flexibility. You can tailor your sitemap to fit your website’s unique needs.
Some popular third-party tools for creating sitemaps include [Tool Name 1], [Tool Name 2], and [Tool Name 3]. They have easy-to-use interfaces and work well with your website. They also generate sitemaps thoroughly.
Static vs. Dynamic Sitemaps
When creating a sitemap, you must decide between static or dynamic. A static sitemap is updated manually when your website changes. A dynamic sitemap updates automatically, which is handy for sites with frequent updates or lots of content.
Think about your website’s nature, how often it changes, and what you prefer. This will help you choose the right sitemap type.
In the next section, we will discuss how to submit your sitemap to search engines for indexing.
Submitting the Sitemap to Search Engines
After making your sitemap, you need to submit it to search engines. You can do this through webmaster tools provided by search engines.
For example, you can submit your sitemap to Google Search Console, Bing Webmaster Tools, and Yandex.Webmaster for better visibility and indexing.
Each search engine’s webmaster tools have specific instructions on how to submit sitemaps.
Conclusion
Creating a site map is key to optimizing your website for enhanced visibility and search engine performance. By following the SEO tips and best practices in this guide, you can improve your website’s indexing efficiency. This ensures search engines prioritize your most valuable content.
An optimized site structure, achieved through a well-designed and SEO-friendly site map, helps search engine bots crawl and index your website better. This leads to more organic traffic and higher rankings in search engine results.
Remember to include all relevant and indexable pages in your site map while avoiding thin or duplicate content. By focusing on high-quality and valuable content, you can maximize the visibility and indexing of your website’s most important parts.
Implementing a complete site map and optimizing your site structure are key steps in your SEO strategy. By creating a clear roadmap for search engines, you can enhance your website’s search performance. This attracts more organic traffic, ensuring the long-term success of your online presence.
FAQ
What is a sitemap?
A sitemap is an XML or HTML file that lists your website’s URLs. It acts as a digital map for search engine bots.
Why are sitemaps useful?
Sitemaps are useful for improving search engine crawling and indexing of your website. They help search engines find and index all important pages, even if your website is complex.
Who needs a sitemap?
Sitemaps are essential for websites with dynamic content that are updated frequently, large websites with many pages, new websites with few external links, and websites with isolated or poorly linked pages. They are also valuable for websites with rich media content, such as images and videos.
What should I include in a sitemap?
Include only indexable pages with valuable content in your sitemap. Avoid including thin or duplicate content, paginated pages, parameter or session ID-based URLs, site search result pages, and archived pages.
What are the components of a sitemap?
A sitemap has XML tags like and . The tag is for a single URL. It has sub-tags for the URL, last update, how often it changes, and its importance.
Are there any sitemap extensions?
Yes, there are extensions like XML Image Sitemaps, XML Video Sitemaps, and Google News Sitemaps. They help index multimedia content better.
How can I create a sitemap?
You can make a sitemap by hand or use tools. You can write the XML or HTML code yourself. Or, you can use CMS, eCommerce platforms, plugins, or third-party tools.
How do I submit my sitemap to search engines?
To submit your sitemap, use webmaster tools. Google Search Console, Bing Webmaster Tools, and Yandex.Webmaster are good options.
What is the importance of site map creation?
Creating a site map is key for better website indexing and search performance. It helps search engines find and index your content more efficiently. This makes your important pages more visible online.